Comprehensive Treatment Technologies for Spray Coating Industry Exhaust Gases
Spray coating operations generate exhaust gases containing benzene series, esters, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and suspended particulate matter, posing significant threats to ecosystems and human health. With increasingly stringent environmental regulations, the industry urgently requires efficient and cost-effective exhaust gas treatment systems. Current technologies have evolved from single purification methods to multi-stage collaborative treatment systems, combining physical adsorption, thermal decomposition, and phase-change processes to achieve compliant emissions. This article provides a detailed analysis of mainstream treatment technologies and innovative applications, offering insights for pollution control in the industry.
- Mainstream Technologies for Spray Coating Exhaust Treatment
(I) Physical Adsorption Technologies
- Activated Carbon Adsorption Process
Leveraging the unique honeycomb structure of activated carbon, its extensive microporous network effectively captures organic molecules. This technology achieves over 95% removal efficiency for VOCs, particularly targeting benzene derivatives and ester-based solvents. Practical applications require a scientific adsorbent regeneration system, such as steam or inert gas desorption, reducing material loss by 30%–40%. Proper disposal protocols for spent activated carbon are critical to avoid secondary pollution.
(II) Thermal Decomposition Technologies
2.1 High-Temperature Incineration Systems
Utilizing auxiliary fuels (e.g., natural gas), exhaust gases are heated to 760–820°C for oxidative decomposition, suitable for high-concentration organic waste gases. Integrating waste heat recovery systems can reduce energy consumption by over 25%. However, high-temperature conditions may generate NOx byproducts, necessitating SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitrification devices.
2.2 Catalytic Oxidation Units
Noble metal catalysts (e.g., platinum, palladium) lower reaction temperatures to 300–400°C, achieving 40% energy savings compared to traditional combustion. Case studies show purification efficiency exceeding 98.5% for toluene concentrations >1,500 mg/m³. Regular catalyst activation is essential to maintain reactivity.
(III) Phase-Change Treatment Technologies
3.1 Low-Temperature Condensation Recovery
Three-stage gradient cooling (0°C, –25°C, –70°C) enables fractional condensation of VOCs, achieving >85% recovery rates for high-boiling-point organics. Automotive coating lines report solvent recovery rates of 15%–20% of raw material usage, demonstrating significant economic benefits.
3.2 Absorption Purification Systems
Specialized chemical absorbents (e.g., composite surfactant solutions) facilitate gas-liquid mass transfer, achieving 60%–75% efficiency for water-soluble VOCs. pH regulation systems and evaporative crystallization units are required for spent absorbent treatment.
- Integrated Treatment Solutions
(IV) Combined Process Applications
Adsorption-catalytic regeneration systems integrate activated carbon adsorption with catalytic oxidation, forming a closed-loop treatment process. A typical configuration includes: pre-treatment tower (paint mist removal) → zeolite rotor (VOCs enrichment) → catalytic combustion chamber (oxidative decomposition) → heat recovery unit. Operational data indicate 99.2% removal efficiency for inlet concentrations of 800 mg/m³, with 45% lower energy consumption compared to standalone catalytic combustion.
- Key Factors for Process Optimization
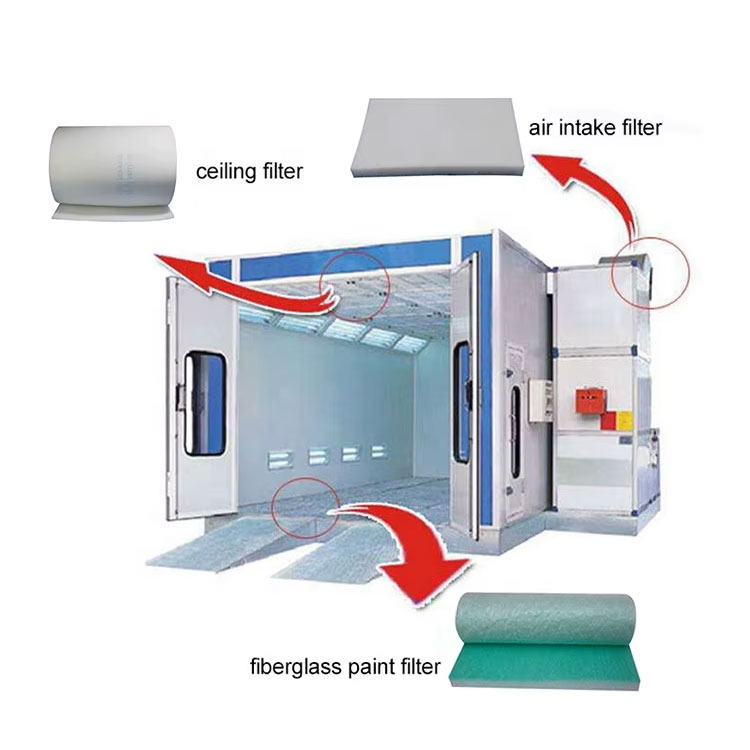
(V) Pre-Treatment Innovations
Dual pre-treatment combining dry filtration (labyrinth-style filter pads) and wet scrubbing (Venturi water curtains) elevates paint mist removal efficiency to 99.9%. An aerospace manufacturing case study shows this combination extends catalytic bed lifespan by 3.5 times.
(VI) Intelligent Monitoring Systems
Online monitoring networks integrate FID (Flame Ionization Detector) analyzers, differential pressure sensors, and temperature transmitters for real-time efficiency tracking. PLC systems enable automatic adsorption saturation alerts and catalytic bed temperature regulation, ensuring stable compliance with emission standards.
- Industry Development Trends
Current advancements focus on resource recovery, with emerging solutions such as zeolite molecular sieve adsorbents, low-temperature plasma-catalytic synergy, and biofilter combinations gaining traction. IoT-based remote operation platforms and digital twin technologies are reshaping maintenance models, improving treatment efficiency by 15%–20% while reducing operational costs by 30%.
Modern spray coating exhaust treatment has evolved into comprehensive solutions spanning source control to end-of-pipe management. Enterprises should adopt tailored processes based on production characteristics and establish full-process management systems to meet environmental standards while maximizing resource efficiency.